
|
genNoise
|



|
|
|
| Input
|
|
|
| An integer between 0 and 116 specifying the input image frame number. A value of 0 represents the DMA memory buffer of the video device. Values in the range of 100-116 correspond to hidden frames.
|
|
|
| Output
|
|
|
| An integer between 1 and 116 specifying the output image frame number. Values in the range of 100-116 correspond to hidden frames.
|
|
|
| Sigma
|
|
|
| A positive floating variable or constant specifying the standard deviation ó for the statistical distribution of noise. The larger this value is, the bigger the noise variations will be.
|
|
|
| Density
|
|
|
| An enumerated integer that describes the type of the noise distribution. Must be on of the following values:
|
|
|
| NS_UNIFORM – uniformly distributed white noise of the selected variance. The amplitude range of the noise is limited to the value of |
| NS_GAUSS – Gaussian white noise of the selected local variance. The intensity distribution of noise is defined by the following equation:
|
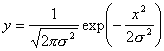
|
| NS_EXPONENT – exponential white noise of the selected local variance. The intensity distribution of noise is defined by the following equation:
|
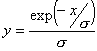
|
| NS_POISSON – Poisson noise generated from the image data. The intensity distribution of noise is defined by the following equation:
|
| Default value: NS_UNIFORM
|
| This set of statements continuously grabs an image and adds to it a uniform noise with the standard deviation 20:
|
|
|
| do
|
| grabim (100)
|
| gennoise(100,1,20,0)
|
| loop
|